Automated Radiomics Based Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Grade Classification from Biparametric MRI
Announcing Our Latest Research: Automated Radiomics Based Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Grade Classification from Biparametric MRI
We are thrilled to unveil our latest research, “Automated Radiomics Based Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer (csPCa) Grade Classification from Biparametric MRI.” This pioneering study addresses critical challenges in prostate cancer diagnosis by leveraging advanced imaging techniques and machine learning to improve accuracy and reduce reliance on contrast agents.
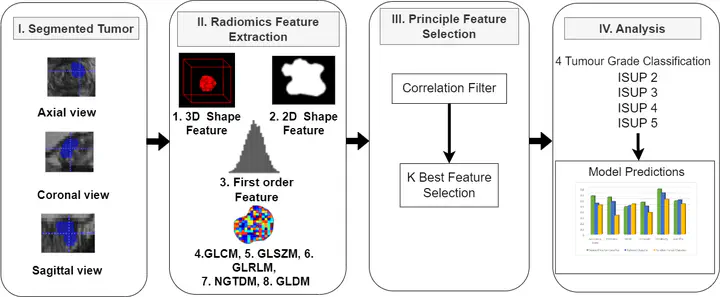
In this research, we introduce a fully automated framework that utilizes biparametric MRI (bp-MRI) to segment csPCa lesions and classify their grades based on radiomics features. This approach counters the limitations of multiparametric MRI (mp-MRI), such as the use of gadolinium-based contrast agents that can lead to nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, and the complexity of image interpretation. Our framework extracts 124 radiomics features from eight categories and employs these features to train several machine learning classifiers, including SVM, KNN, Bayesian, XGBoost, and Random Forest. Among these, the XGBoost classifier demonstrated remarkable performance, achieving a 96% accuracy in distinguishing between clinically significant (ISUP 4+5) and non-significant (ISUP 2+3) prostate cancer based on the predicted maps generated by our segmentation method.
This study underscores the potential of bp-MRI combined with radiomics and machine learning to revolutionize prostate cancer diagnostics. By minimizing the need for contrast agents and enhancing diagnostic accuracy, our method paves the way for safer and more efficient clinical workflows.
We invite you to delve into our full paper for a comprehensive understanding of our methodologies, experimental results, and the implications of our findings. We welcome your feedback and look forward to potential collaborations as we continue to innovate in the field of medical imaging.
Authors: Md Rakibul Islam, Abdullah Nazib, Riad Hassan, Kien Nguyen, Clinton Fookes, Md Zahidul Islam
Affiliations: Islamic University, Bangladesh; Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology; Green University of Bangladesh; Queensland University of Technology